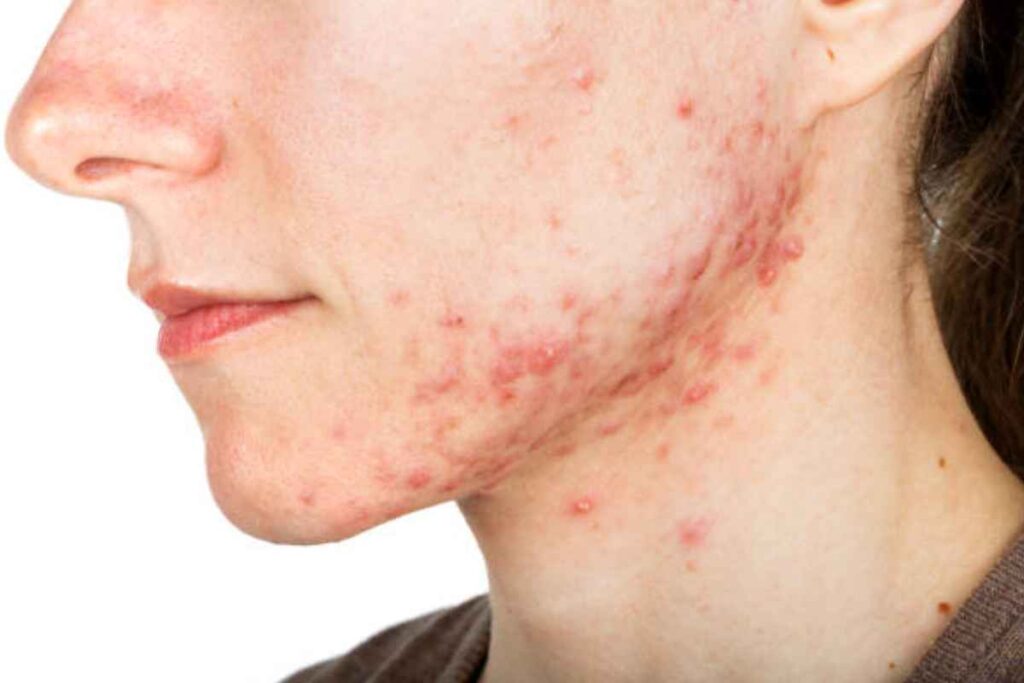
Rosacea is a common skin condition often mistaken for acne or skin sensitivity, leading to delays in diagnosis and worsening symptoms such as redness, visible blood vessels, and breakouts. Because symptoms and associated triggers vary from person to person, pinpointing the cause of flare-ups can be challenging. However, learning more about the condition can help you recognise triggers and manage symptoms effectively. This article will give you everything you need about rosacea, including treatments to help manage your symptoms. Let’s start with the basics.
What is Rosacea?
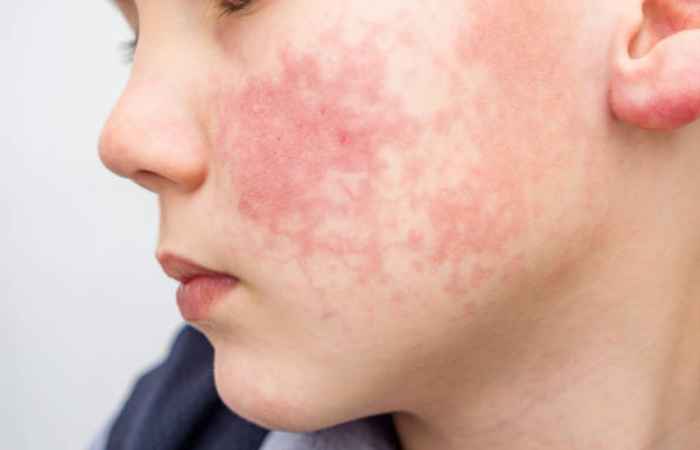
Rosacea is a chronic skin chaos that primarily touches the face. It typically develops in cycles of flare-ups and remissions, meaning symptoms may appear and disappear over time. Rosacea is more common in people with fair skin and is often aggravated by sun exposure, stress, spicy foods, or alcohol. Although there is no cure, proper treatment and lifestyle changes can help effectively control symptoms.
What are the Types of Rosacea?
Rosacea is classified into four main types:
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR) – This type is marked by persistent redness (erythema) and visible blood vessels (telangiectasia), mainly on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. The skin may feel sensitive, dry, or rough, and flushing episodes can last longer. Common triggers include sun exposure, heat, spicy foods, alcohol, and emotional stress.
- Papulopustular Rosacea (Acne Rosacea) – Often confused with acne, this type causes red bumps (papules) and pus-filled pimples (pustules) that appear in cycles. Unlike acne, it doesn’t cause blackheads or whiteheads. The skin may also be oily, swollen, and sensitive, with a burning or stinging sensation. It is more common in middle-aged women but can affect anyone.
- Phymatous Rosacea – This rarer form causes thickened, bumpy, and rough skin, primarily on the nose (rhinophyma), but it can also develop on the chin, forehead, ears, or cheeks. It is more common in men and tends to develop gradually, leading to enlarged oil glands and a bulbous, distorted appearance of affected areas.
- Ocular Rosacea affects the eyes, leading to soreness, irritation, dryness, and a burning or gritty sensation. The eyelids may become swollen, and small cysts or crusting can form along the edges. More severe gears can cause blurry vision, light sensitivity, and complications like corneal damage if left untreated. Ocular rosacea is often overlooked as an eye infection or allergy, delaying proper treatment.
Since rosacea symptoms can overlap, some people may experience a combination of these types.
What Causes Rosacea?
The exact reason for rosacea is not fully unspoken, but students believe it results from genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Certain factors may contribute to its development or make symptoms worse, including:
- Sun Exposure – Ultraviolet (UV) rays can damage the skin and trigger flare-ups, making sun protection essential.
- Hot or Cold Weather – Extreme temperatures, strong winds, and humidity changes can worsen symptoms.
- Spicy Foods and Hot Beverages can dilate gore vessels, increasing redness and flushing.
- Alcohol and Caffeine – Red wine and hot drinks like coffee or tea may cause facial flushing.
- Emotional Stress – Anxiety, anger, and embarrassment can trigger episodes of redness.
- Exercise – Intense physical activity may lead to flare-ups, particularly in hot conditions.
- Skincare Products and Cosmetics – Harsh cleansers, fragrances, and alcohol-based products can irritate sensitive skin.
- Medications – Some drugs, such as blood gravity medications that dilate blood vessels, may worsen symptoms.
- Demodex Mites and Bacteria – Higher levels of Demodex mites, which naturally live on the skin, have been linked to rosacea. Certain bacteria may also contribute to inflammation.
Not everyone with rosacea reacts to the same triggers, so identifying triggers that affect you and avoiding them can help manage flare-ups effectively.
What are the Symptoms of Rosacea?
Rosacea symptoms can vary from person to person, but the most common signs include:
- Facial Redness (Erythema) – Persistent redness, often on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin, which may resemble a sunburn that doesn’t go away.
- Visible Blood Vessels (Telangiectasia) – Small, broken blood vessels become noticeable on the skin’s surface, especially in fair-skinned individuals.
- Flushing – Sudden episodes of intense redness that may feel warm or uncomfortable, triggered by heat, stress, or certain foods.
- Bumps and Pimples – Red, acne-like bumps (papules) and pus-filled pimples (pustules) that can appear during flare-ups, though rosacea does not cause blackheads.
- Skin Sensitivity – Burning, stinging, or itching sensations, especially after using certain skincare products or exposure to triggers.
- Thickened Skin (Phymatous Changes) – In some cases, particularly in men, the skin may become thickened and bumpy, most commonly on the nose (rhinophyma).
- Eye Irritation (Ocular Rosacea) – Red, dry, or watery eyes, swollen eyelids and a gritty or burning sensation, which may be mistaken for allergies or an eye infection.
What Are the Treatment Options for Rosacea?
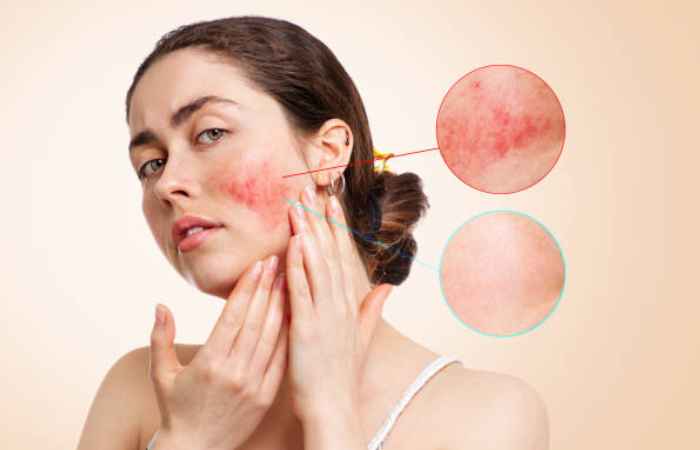
Rosacea cannot be cured, but its indications can be effectively managed with the proper treatment. Combining medical treatments, skincare routines, and lifestyle adjustments can help decrease flare-ups and improve skin health.
Medical Treatments
- Topical Treatments – Doctors may prescribe creams or gels that help reduce redness, inflammation, and acne-like bumps. These are typically applied directly to affected areas to soothe irritation and improve skin texture.
- Oral Medications – Oral medications may be recommended for moderate to severe cases to control inflammation and prevent flare-ups. These treatments can help reduce persistent redness and bumps that do not respond to topical applications.
- Laser and Light Therapy – These treatments use targeted light to reduce visible blood vessels and persistent redness. They are handy for individuals with prominent facial veins or long-term redness that does not improve with medication.
- Eye Care for Ocular Rosacea – If rosacea affects the eyes, lubricating eye drops or prescription treatments may be needed to relieve dryness, irritation, and inflammation. In some cases, a doctor may recommend additional eye care treatments.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Identifying and Avoiding Triggers – Common rosacea triggers include spicy foods, alcohol, caffeine, extreme weather conditions, stress, and certain skincare products. Keeping a symptom diary can help identify which factors worsen flare-ups.
- Using a Gentle Skincare Routine – Harsh skincare products can aggravate rosacea symptoms. It’s best to use mild, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturisers. Avoid exfoliating scrubs, alcohol-based toners, and other irritating ingredients.
- Protecting the Skin from Sun Exposure – Sun exposure is a common trigger for rosacea flare-ups. Wearing a broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, using protective clothing, and seeking shade when outdoors can help protect sensitive skin.
- Managing Stress and Lifestyle Factors – Stress is a known trigger for rosacea flare-ups. Relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels and reduce symptoms.
- Dietary Adjustments – Some people through rosacea find that certain foods, such as hot beverages, spicy foods, and alcohol, worsen their symptoms. Avoiding these activities and maintaining a balanced diet can help keep flare-ups under control.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Rosacea symptoms can vary in severity, and while mild cases may be managed with existing changes, medical attention is necessary in certain situations. Consider seeing a doctor if:
- Redness or Flushing Becomes Persistent – A doctor can recommend treatments to prevent further progression if facial redness does not go away and continues to worsen.
- Bumps or Pustules Develop – Acne-like breakouts, swelling, or persistent irritation may require medical treatment to prevent worsening symptoms.
- Visible Blood Vessels Appear – If broken or visible blood vessels become more noticeable, medical treatments such as laser therapy may be needed.
- Eye Discomfort or Vision Issues Occur – Ocular rosacea can cause dryness, irritation, swelling, or blurred vision. If you experience these symptoms, an eye specialist may need to assess your condition.
- Home Remedies and Over-the-counter Products Are Not Helping – A dermatologist can offer prescription treatments tailored to your symptoms if skincare adjustments and trigger avoidance do not provide relief.
Early medical intervention can help prevent rosacea from worsening and make it easier to manage in the long term.
Consult Today
Treating rosacea can be a challenging experience, especially if symptoms persist despite your best efforts. If rosacea affects your self-confidence or daily life, seeking expert help can make all the difference. Book a consultation today and take the first step toward clearer, healthier skin.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can rosacea spread to other parts of the body?
Rosacea primarily affects the face, but in most cases, symptoms can extend to the neck, chest, scalp, or ears. However, it does not spread like an infection.
Is rosacea contagious?
No, rosacea is not contagious. It is a chronic skin condition that changes due to internal and external factors but cannot be passed from person to person.
Can diet affect rosacea flare-ups?
Yes, certain foods and drinks can trigger flare-ups. Spicy foods, alcohol, hot beverages, and foods high in histamines are common culprits. Keeping a food diary can help classify specific triggers.
Does it get worse with age?
Without proper management, rosacea can become more severe over time. Flare-ups may become more frequent, and symptoms like redness and visible blood vessels can develop more pronounced. Early treatment can help control its progression.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage rosacea?
Adopting a gentle skincare routine, using sun protection, managing stress, and avoiding known triggers can help reduce flare-ups. Staying hydrated and maintaining a sensible diet can also support skin health.
Can makeup or skincare products make rosacea worse?
Certain skincare products and cosmetics containing alcohol, fragrance, or harsh ingredients can aggravate. Opting for gentle, fragrance-free products for sensitive skin can help prevent irritation.
Is rosacea linked to any other health conditions?
Some studies suggest a possible link between rosacea and gastrointestinal disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and migraines. However, more research is needed to understand these associations fully.
Can stress trigger symptoms?
Yes, stress is a common trigger for rosacea flare-ups. Practising relaxation methods such as meditation, deep breathing, and regular exercise can help manage stress-related symptoms.
Are there any tests to diagnose?
There is no specific test for rosacea. A dermatologist typically diagnoses it by physical examination and discussing symptoms, triggers, and medical history.
Can rosacea be permanently cured, or is it a lifelong condition?
It is a chronic condition with no permanent cure, but its symptoms can be effectively managed with proper treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and trigger avoidance. Early intervention can help keep flare-ups under control.